PEM Core is a monthly curriculum focused on reviewing PEM Certification Exam (Boards) Content. It is not intended to be a complete review of a case or topic, but rather “hits the high points” about a board topic from the The American Boards of Pediatrics Pediatric Emergency Medicine Content Outline.
Orthopedic Trauma makes up of 10-15% of Emergency Department visits. This month on PEM Core, we are discussing the management principals of extremity trauma.
The Initial Approach
As in all cases of trauma, start with the ABC’s and/or ATLS. Extremity deformities are a classic distracting injury, therefore a standardized approach will help prevent misses.
Assess for Emergent Complications
Neurovascular Compromise
Amputation
Open Fractures
Presence of Compartment Syndrome
Unrecognized Bleeding (Pelvic and/or Femur Fractures)
Key History Components
Mechanism
Timing
Description
Subjective Dysfunction
(Injured extremity vs uninjured extremity)
Key Physical Exam Components
Compare Two Extremities
Palpation
Range of Motion
Loading (Axial and Transverse)
Criteria for Radiographic Evaluation
Point Tenderness
Pain with Loading
Significant Amount of Swelling
Very Limited or No Range of Motion
The Upper Extremity
Clavicle Fracture
Usually from direct trauma, falls against the humerus, or FOOSH
Exam Features:
Carrying the injured arm
Focal tenderness over the clavicle
Positive Scarf Sign
Diagnosis:
X-ray
Point of Care Ultrasound: Sensitivity 95% and Specificity of 96% with similar pain scores. [1]
Management:
Emergent:
When proximal or sternoclavicular joint dislocation with posterior displacement (risk of great vessel injury and/or impingement)
Non-Emergent:
Immobilize, RICE, Pain Control (tylenol/ibuprofen)
Orthopedics Referral if distal clavicle fracture
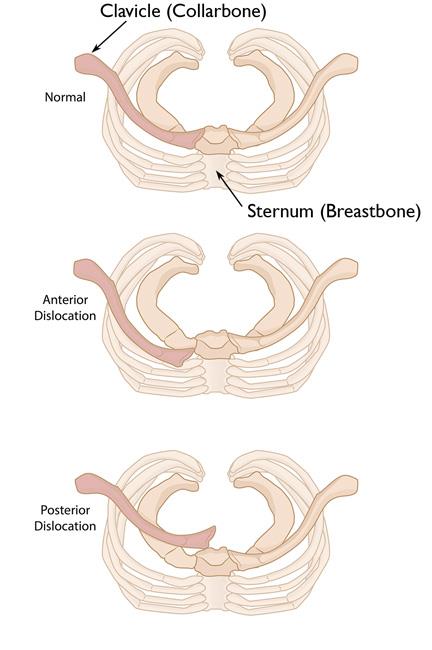
Posterior dislocation can lead to compression of Major Vessels, the Esophagus, the Trachea.
Be suspicious if the patient is having stridor, tachypnea, dysphagia, or significant tachypnea
Image taken from https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/sternoclavicular-sc-joint-disorders/
Separated Shoulder
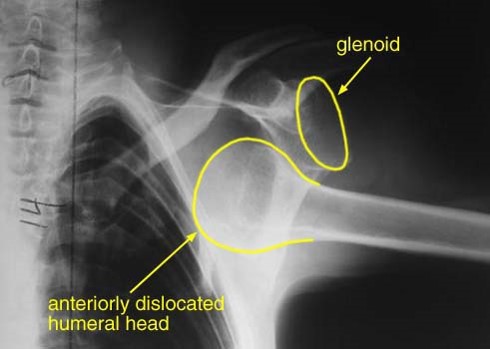
AP XR image of anterior shoulder dislocation.
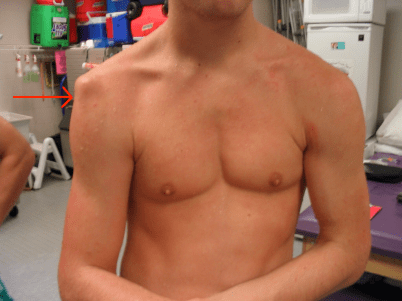
Sulcus sign. Image from https://b-reddy.org/should-pitchers-deadlift/
Ligamentous injury to the acromioclavicular joint +/- the coracoclavicular joint.
>95% are anterior dislocations in adolescents
Usually injured from external rotation and abduction with force applied posteriorly
Exam Features:
Significant pain
High levels of anxiety
No ROM with a sulcus sign
Diagnosis:
X-ray
Point of Care Ultrasound
Management:
Reduction:
Be sure to provide adequate analgesia and muscle relaxation.
Intraarticular Lidocaine is a great alternative to conscious sedation.
See video below for 10 different techniques by Larry Mellick at the Medical College of Georgia
Complications:
Bankart Lesion: a tear of glenoid labrum
Hill-Sachs Fracture: an indentation fracture to the humerus
Proximal Humerus Fracture
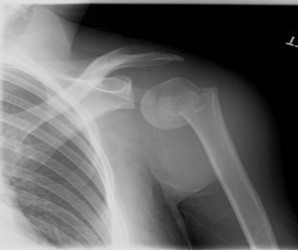
AP XR image of a left proximal humerus fracture.
Usually from a direct blow, fall on adducted arm or external rotation with abduction and posterior force applied.
Proximal fractures are more common in the 5-11 year age group.
Exam Features:
Arm held in extension
Significant point tenderness
Painful ROM
Anterior mass as distal fragment is pulled forward by the upper arm muscles
Diagnosis:
X-ray
Point of Care Ultrasound
Management:
Conservative:
Can tolerate 1cm separation, <40 degrees of angulation, no malrotation
Sling and swath
Pain Management
Outpatient Orthopedics follow-up in 1 week
Orthopedics Consultation in the ER if:
Significant displacement
>10yr old
Intra-articular involvement
Elbow Injuries
Dislocation:
Rare in kids (~6%)
Commonly occurs with concurrent fractures
Exam Features:
Obvious deformity
Localized pain and edema
No ROM
Carefully assess for ulnar nerve entrapment and brachial arterial injury
Diagnosis:
X-ray
Management:
Make sure to obtain X-ray to check for associated fracture.
Orthopedics consultation
Prompt reduction required (video below from doctortelemark)
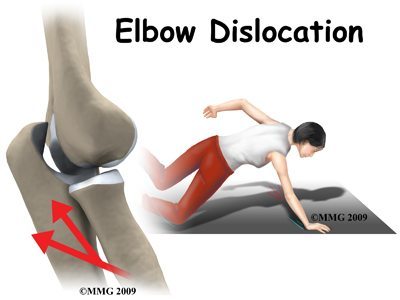
Mechanism of elbow dislocations from LOPT.
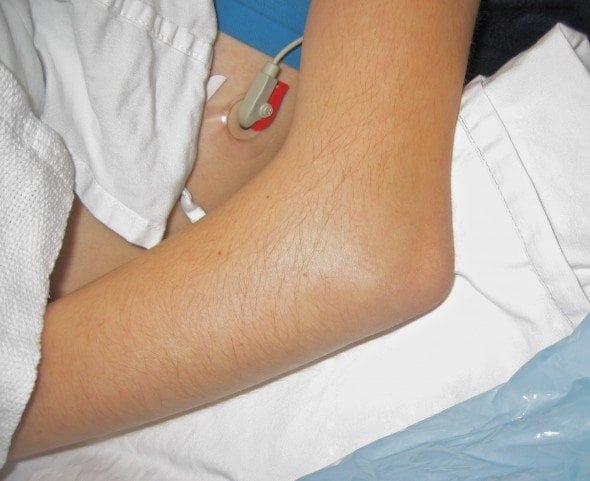
Image of an elbow dislocation from Life in the Fast Lane.
Elbow Fracture: Supracondylar Fractures
Can be difficult to diagnose
Elbow injuries are associated with multiple complications
TRASH Lesions: “The Radiographic Appearance Seemed Harmless”
Exam Features:
Can have an obvious deformity
Swelling (Almost always a sign of underlying injury)
Diagnosis:
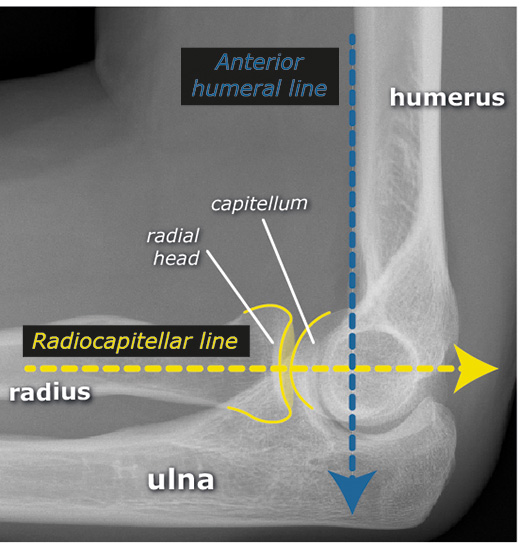
X-ray Findings to Be Aware of:
Radiocapitellar Lines
Anterior Humeral Line
Ossification Centers of the Elbow (CRITOE)
Anterior and Posterior fatpads
Management:
Supracondylar Fractures [2]: Shown below
If displaced, requires closed reduction and casting.
If there is swelling around the elbow, assume injury and discuss with orthopedics
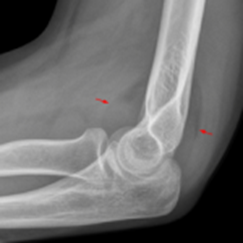
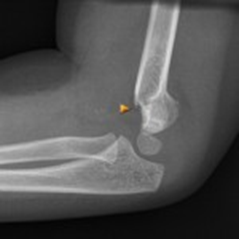
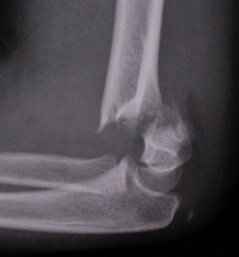
Supracondylar Fractures from Top to Bottom: Type 1 (anterior and posterior fat pads), Type 2 (abnormal anterior humeral line), Type 3 (obvious displacement

CRITOE Elbow Ossification from EMNote.org
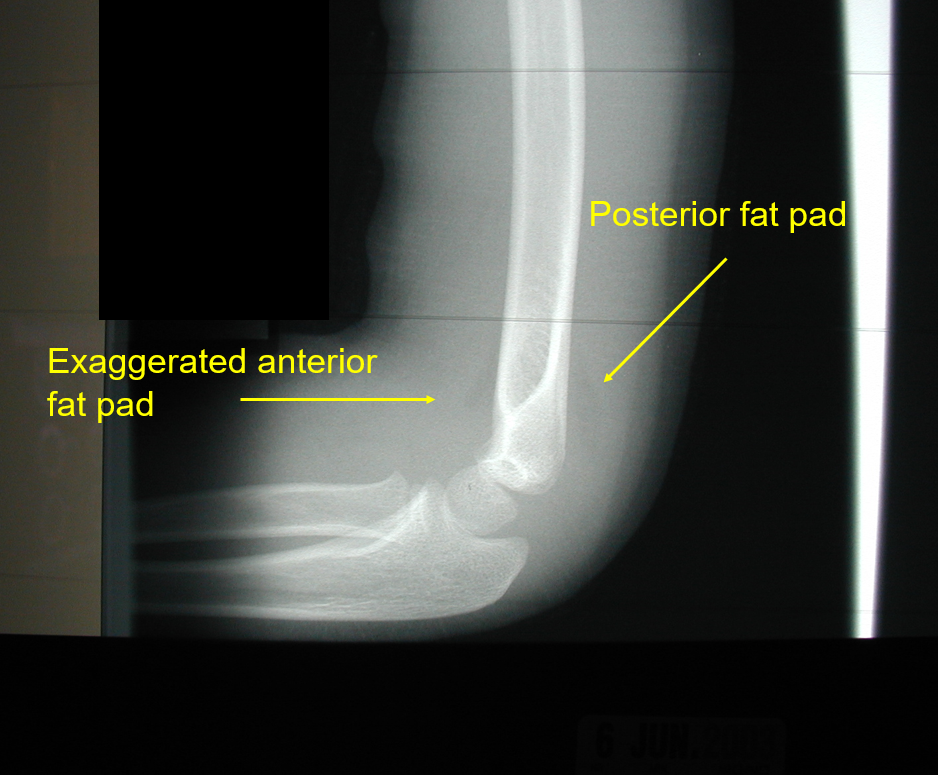
Anterior and posterior fat pads on a supracondylar fracture
Forearm Injuries
Fractures:
Mechanism
Usually FOOSH
Direct Blow
Exam Features:
+/- Deformity
Localized pain and edema
Decreased ROM
Diagnosis:
X-ray
When to Call Orthopedics:
Angulation:
If <8yo
>20°-25° of flexion-extension angulation
>10°of radial-ulnar deviation
The more proximal the injury, the less angulation is tolerated
Malrotation will not remodel
Salter Harris III or above
Open Fractures
Neruovascular compromise
Monteggia or Galeazzi Fracture
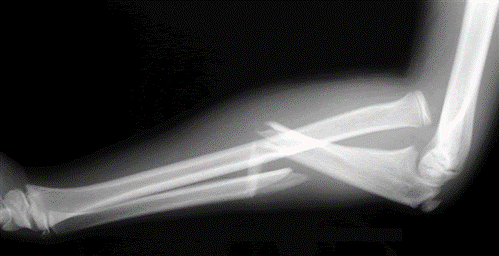
Monteggia Fracture: Ulnar fracture with radial head dislocation
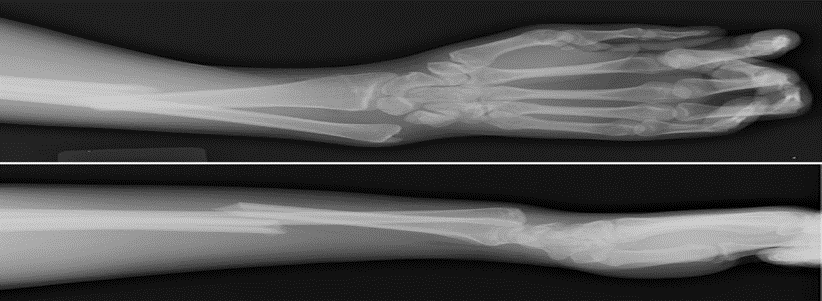
Galeazzi Fracture: Fracture of the radius with ulnar head dislocation
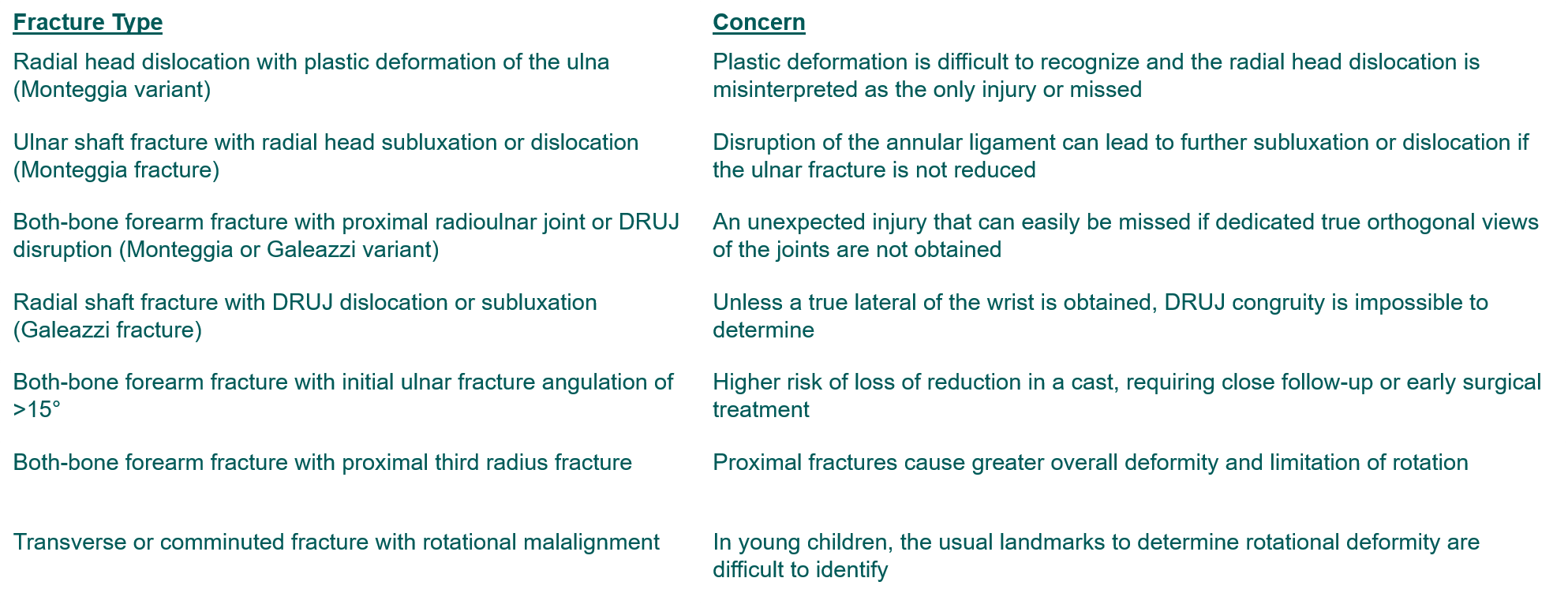
Other Complicated Forearm Fractures from Zlotolow J Hand Surg Am 2012
References
Other Images taken from Dr. Gary Geis and his Extremity Trauma Lecture.
Cross KP, et al. Acad Emerg Med. 2010 Jul;17(7):687-93.
Mulpuri J Pediatr Orthop 2012
Zlotolow J Hand Surg Am 2012; Bae J Hand Surg Am 2008
Dr. A van der Plas (MSK radiologist Maastricht UMC) http://www.startradiology.com/internships/general-surgery/elbow/x-elbow/
Ossification centers of the elbow https://www.emnote.org/emnotes/ossification-centers-of-the-elbow
Dr Mike Cadogan, last update September 9, 2019 Elbow Dislocation https://litfl.com/elbow-dislocation/
Physical Therapy in Lincoln and Ashland for Elbow Issues. Elbow Dislocation. https://loptonline.com/patient-education/injuries-conditions/elbow-issues/elbow-dislocation/
Should pitchers deadlift? Last Updated On: August 7, 2017 https://b-reddy.org/should-pitchers-deadlift/
Sternoclavicular (SC) Joint Disorders https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/sternoclavicular-sc-joint-disorders/

Ashish Shah is an assistant professor and Pediatrics and Family Medicine Residency Education Director at Rady Children’s Hospital interested in creating PEM 4 all stages of learners caring for children seen in the emergency department



